LDPE vs. HDPE: Comparing Two of the Most Common Polyethylene Types
Polyethylene is one of the most widely used plastics today, thanks to its affordability, ease of processing, and versatility across industries. Polyethylene (PE) comes in several types, each with unique properties suited to specific applications, including:
- Low-density polyethylene (LDPE)
- High-density polyethylene (HDPE)
- Linear low-density polyethylene (LLDPE)
- Very-low-density polyethylene (VLDPE)
- Ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene (UHMWPE)
This article will focus on the two most common forms of polyethylene, LDPE and HDPE, providing a clear comparison to help you decide which might be best for your next project.
HDPE Vs LDPE Comparison
1. Low-Density Polyethylene (LDPE)
LDPE is a lightweight, flexible plastic known for its soft feel and transparency. Due to its malleability and moisture resistance, it’s commonly used for packaging and film applications, like grocery bags and plastic wraps.
Chemical Structure of LDPE
LDPE is produced by polymerizing ethylene gas at high pressure, which creates branching in the polymer chains. This branching prevents the molecules from packing closely, resulting in a lower density and greater flexibility than HDPE.
Properties of LDPE
- Malleable and Elastic: LDPE can stretch considerably, making it suitable for film applications.
- Moisture and Chemical Resistant: It withstands exposure to acids, alkalis, and some solvents, although it is limitedly resistant to hydrocarbons and UV light.
- Low Melting Point: Softens at around 100°C (212°F), which enhances its sealing properties.
- Lightweight: Density ranges from 0.910 to 0.940 g/cm³.
- FDA Compliance: LDPE is often approved for food contact, especially in flexible packaging.
Applications of LDPE
Due to its flexible and lightweight nature, LDPE is widely used in:
- Packaging: Grocery bags, plastic wraps, food containers.
- Industrial Uses: Water pipes, hoses, and insulation for electrical cables.
- Consumer Goods: Toys, six-pack rings, and household items.
2. High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE)
HDPE is a more rigid and durable form of polyethylene. It offers higher strength and is commonly used in products that require excellent toughness, such as pipes, crates, and bottles.
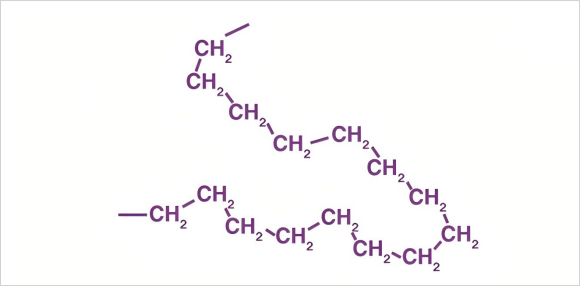
 Chemical Structure of HDPE
Chemical Structure of HDPE
HDPE has a linear structure with minimal branching, allowing its molecules to pack closely. This gives HDPE its high density and tensile strength compared to LDPE.
Properties of HDPE
- Higher Density and Rigidity: HDPE is denser (0.93 to 0.97 g/cm³) and more rigid than LDPE, which makes it ideal for durable goods.
- Chemical and UV Resistance: HDPE resists many solvents, alcohols, acids, and UV rays, making it suitable for outdoor applications.
- Higher Melting Point: Melts around 135°C (275°F), providing more excellent heat resistance than LDPE.
- Tensile Strength: HDPE has a tensile strength of around 4,000 psi, making it one of the most inflexible PE options.
Applications of HDPE
- Industrial and Construction: Pipes, fittings, fuel tanks, and geomembranes.
- Consumer Goods: Milk jugs, detergent bottles, and cutting boards.
- Outdoor Equipment: Playground equipment, outdoor furniture, and storage bins.
3. LDPE vs HDPE: Key Differences
Comparison of Physical Properties
| Property | LDPE | HDPE |
|---|---|---|
| Density | 0.910–0.940 g/cm³ | 0.93–0.97 g/cm³ |
| Melting Point | 105–115°C (221–239°F) | 135°C (275°F) |
| Tensile Strength | 1,400 psi | 4,000 psi |
| Flexural Modulus | 30,000 psi | 200,000 psi |
| Water Absorption | 0.10% | 0.10% |
| UV Resistance | Poor | Moderate to Good |
HDPE offers more durability and strength, making it suitable for demanding applications, while LDPE’s flexibility and low cost are ideal for lightweight packaging.
Benefits and Limitations
- LDPE: Lightweight and easy to process, but prone to UV degradation and limited to lower strength applications.
- HDPE: Strong, durable, and chemical-resistant, but generally less flexible than LDPE.
4. Manufacturing and Processing
Production of LDPE and HDPE
Both LDPE and HDPE are produced by polymerizing ethylene, but they use different methods:
- LDPE Production: LDPE is made by a high-pressure process involving free-radical polymerization, which results in a branched structure.
- HDPE Production: HDPE is produced by a low-pressure process, using catalysts in slurry or gas-phase reactors, creating a more linear structure with minimal branching.
Processing Methods
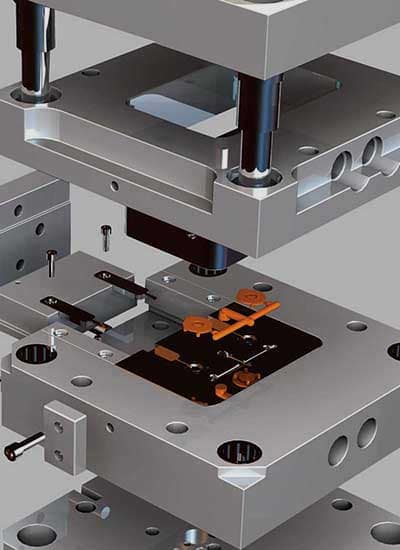
Once produced, LDPE and HDPE are processed into final products using methods like injection molding, extrusion, and blow molding.
- Injection Molding: LDPE and HDPE are melted and injected into moulds, creating solid parts.
- Extrusion: Primarily used for making sheets, films, or tubing.
- Blow Molding: Often used for producing hollow plastic items, like bottles and containers.
Choosing the Right Polyethylene for Your Project
Selecting between LDPE and HDPE depends on your project’s specific demands. LDPE is typically the better choice for applications that need flexibility, lower cost, and lightweight properties. With its strength and chemical resistance, HDPE is ideal for applications that require durability and longevity.











 Chemical Structure of HDPE
Chemical Structure of HDPE
