Enhancing Injection Molding Accuracy Tolerance
Key Strategies and Considerations
Injection molding is an essential industrial technology that enables the production of complex parts with strict tolerances. High precision tolerance in injection molding requires optimal design, material selection, equipment calibration, and process control. These factors must work together to ensure that components fit and perform as expected in their final applications.
This article explores key strategies for improving injection molding accuracy tolerance, with practical tips and insights for achieving the highest level of precision.
Accurate Mold Creation
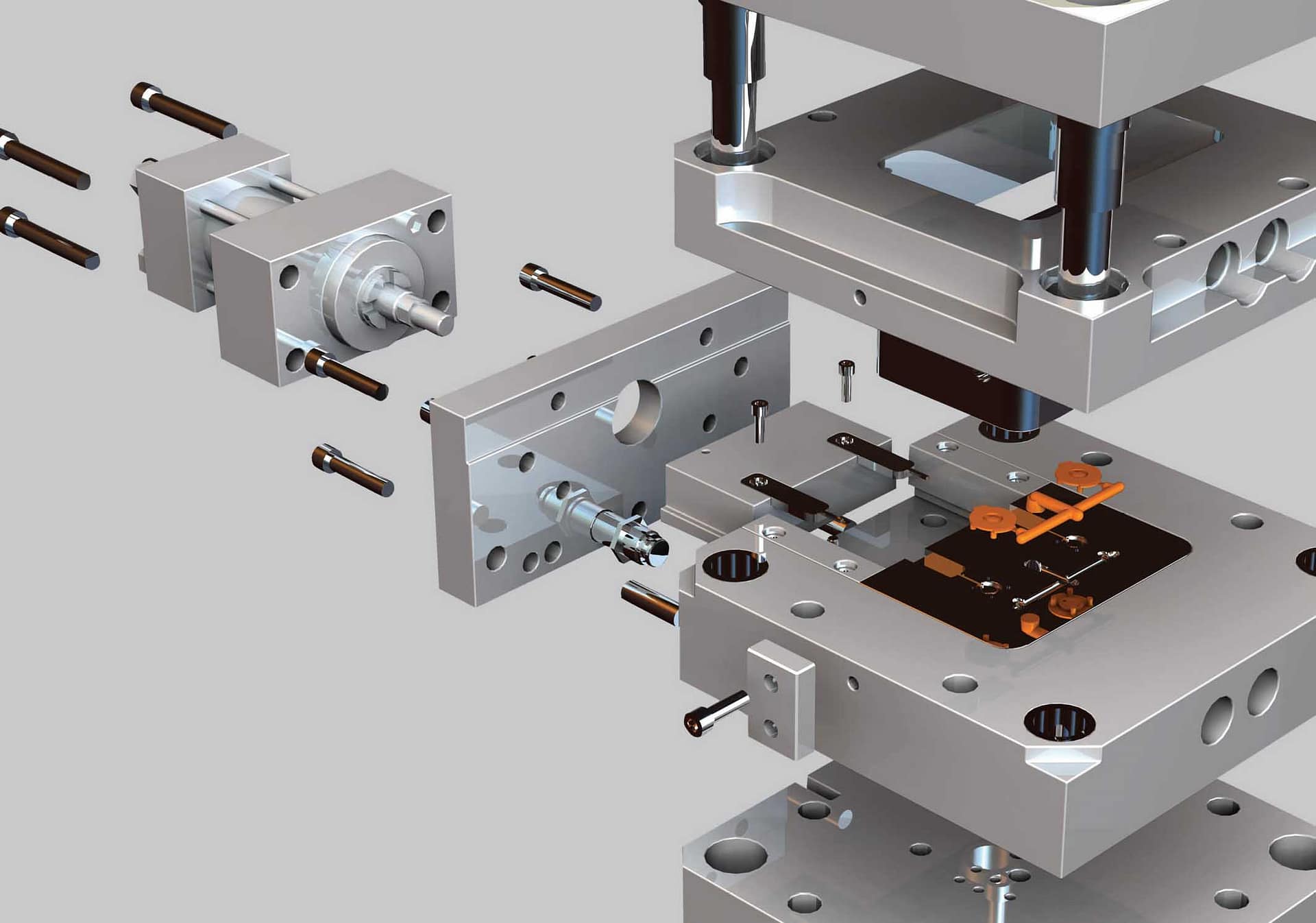
The foundation of precision injection molding lies in the creation of high-quality molds. Mold design and material selection play a crucial role in determining the accuracy tolerance of the molded parts.
High-Quality Mold Steels:
High-quality mold materials such as H13 and NAK80 steel alloys or above are essential to ensure dimensional stability and minimal thermal expansion. These materials offer excellent mechanical properties, high wear resistance, and the ability to withstand high temperatures.
Stringent Tolerances in Mold Design:
The design of the mold components—such as cores, cavities, and inserts—must meet strict tolerances to guarantee a precise fit. By ensuring tight dimensional control and alignment, mold designers can reduce the risk of defects in molded parts.
Optimized Mold Features:
The design should include proper draft angles, radii, and cooling channels to reduce stress during ejection and ensure uniform material flow. The mold’s gating, runner, and venting systems must also be carefully designed to minimize internal stresses and prevent defects such as warping or improper filling.
Spotting Machine for Precise Fitting:
After manufacturing the mold components, a spotting machine precisely aligns and fits the core and cavity halves. This step helps ensure the mold meets the desired tolerances and is ready for production.
Injection Molding Accuracy Tolerance
The injection position accuracy, specifically the pressure holding endpoint, achieves a remarkable precision of less than 0.03mm. Furthermore, the tie rod’s force balance exhibits a high accuracy level, with a less than 1% deviation. The pre-moulding position accuracy also meets stringent standards, with a less than 0.03mm precision.
The maximum mold force is carefully controlled to ensure a less than 0.005mm tolerance, guaranteeing precise and consistent molding outcomes. Moreover, the temperature control accuracy of the barrel and screw is meticulously maintained within a range of less than ±0.5℃, facilitating optimal processing conditions. These exact tolerances and accuracies contribute to achieving high-quality results in the injection moulding process.
Clamping force: High injection pressures are often necessary in precision injection molding to ensure proper mold filling and accurate replication of intricate details.
Measurement accuracy: To maintain high stability in plastic products, it is essential to ensure consistent and precise injection of the hot melt plastic into the mold cavity during the injection molding. Achieving uniformity in each injection cycle is crucial to meeting the desired accuracy tolerance and producing consistent, high-quality plastic parts.
Injection speed: Injection speed is an important indicator of precision injection molding machines and injection molding accuracy tolerance.
Injection pressure: Precision injection requires an enormous injection pressure to improve the compactness of plastic parts, reduce shrinkage and deformation, and ensure the accuracy of parts.
Holding pressure: holding pressure greatly influences precision plastic parts and injection molding accuracy tolerance.
Mold temperature: The temperature change of the cavity surface should be controlled within ±1°C, which is the injection molding accuracy tolerance.
Several factors contribute to maintaining consistent injection of the hot melt plastic:
Injection Speed and Pressure: Controlling the injection speed and pressure is critical to consistently filling the mold cavity. By maintaining a stable and controlled injection speed and pressure, the flow of the molten plastic can be regulated, ensuring that each cavity is filled uniformly.
Melt Temperature and Viscosity: Maintaining consistent melt temperature and viscosity of the plastic material is vital. This can be achieved through precise temperature control of the barrel and screw in the injection molding machine. Consistent melt properties ensure the material flows smoothly and uniformly into the mold cavity.
Injection Time and Dosing: Accurate control of the injection time and dosing of the plastic material is necessary to ensure consistent volume and weight of the injected melt. This helps achieve consistent dimensions and weight for the molded parts.
Mold Design and Venting: Proper mold design, including the layout of gates, runners, and vents, is crucial in achieving uniform filling of the mold cavity. Adequate venting helps prevent air entrapment and ensures a consistent flow of the plastic material.
A plastic injection mold is paramount as a tool for injection molding, as its quality directly impacts the final product’s quality. Simultaneously, the mold cost constitutes a substantial portion of the production cost for an injection molder. Short mold lifespans and inadequate precision compromise product quality and result in significant wastage, including material and labor waste, during plastic injection molding. Consequently, extending the service life of injection molds significantly reduces the cost of plastic products, enhances tooling productivity, and improves overall company competitiveness.
Injection Molding life
During the plastic injection molding process, the elevated temperature and pressure conditions can lead to the decomposition of certain plastics, releasing corrosive gases. These gases have the potential to corrode and damage the surface of the mold. Excessive wear of the mold can cause various issues, such as substandard shape, dimensional accuracy, the surface finish of the plastic parts, and severe flashing. When mold is extensively damaged or worn beyond repair, mold failure becomes inevitable. The service life of a mold refers to the number of molding cycles or the total number of parts produced before the mold reaches a state of failure. An injection mold is typically designed to have a service life exceeding 300,000 cycles.
Injection Molding Accuracy Tolerance
1. Factors that need to be considered in mold tool design
To maintain the accuracy of plastic injection molds under injection pressure and clamping force, the feasibility of grinding, grinding and polishing the cavity parts must be considered when designing the mold structure. Although the processing of the plastic injection mold cavity and core has reached high precision requirements, and the shrinkage rate is the same as expected; However, due to the centre offset during molding, the relevant dimensions of the inner and outer sides of the molded product are challenging to meet the design requirements of plastic parts. To maintain the dimensional accuracy of the front and rear mold cavities on the parting surface, in addition to setting the standard guide pillar and guide sleeve centring, the positioning blocks such as conical positioning pin or wedge block must be added to ensure the accurate and reliable positioning of the plastic injection mold.
2. The material required for plastic injection molds
The material for making plastic injection moulds should be high-quality alloy tool steel with high mechanical properties and low thermal creep for injection moulding accuracy tolerance. The mold material for making the cavity and runner should be selected through strict heat treatment with high hardness, good wear resistance, strong corrosion resistance, and thermal deformation resistance. At the same time, the difficulty and economy of mechanical and electrical processing should also be considered. To prevent ageing changes and change the dimensional accuracy of plastic injection moulds, it is necessary to specify tempering treatment or low-temperature treatment to reduce the residual tissue of the heat treatment of the mould material when designing the mould.
The design should consider the possibility of repair for the vulnerable parts of the plastic injection mold, especially the cavity and core, to maintain the mold’s high accuracy after repair.












No comment