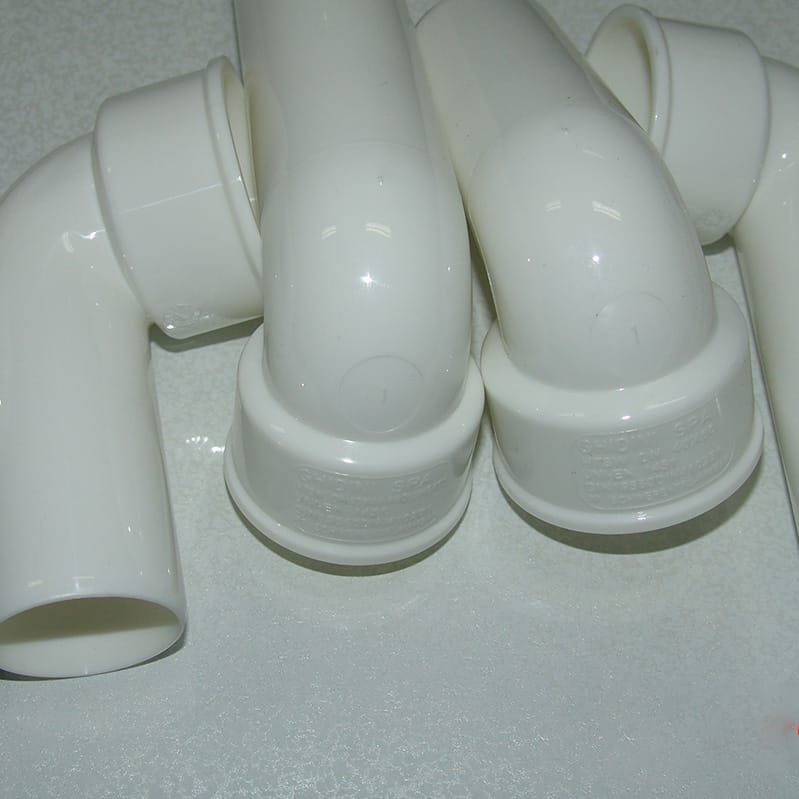
PVC pipe fitting molding
PVC pipe fitting molding refers to producing plastic pipe fittings using injection moulding technology, with polyvinyl chloride (PVC) as the primary material.
PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride) is an increasingly popular thermoplastic polymer due to its durability, chemical resistance, and cost-effectiveness—qualities that make it suitable for various piping applications.
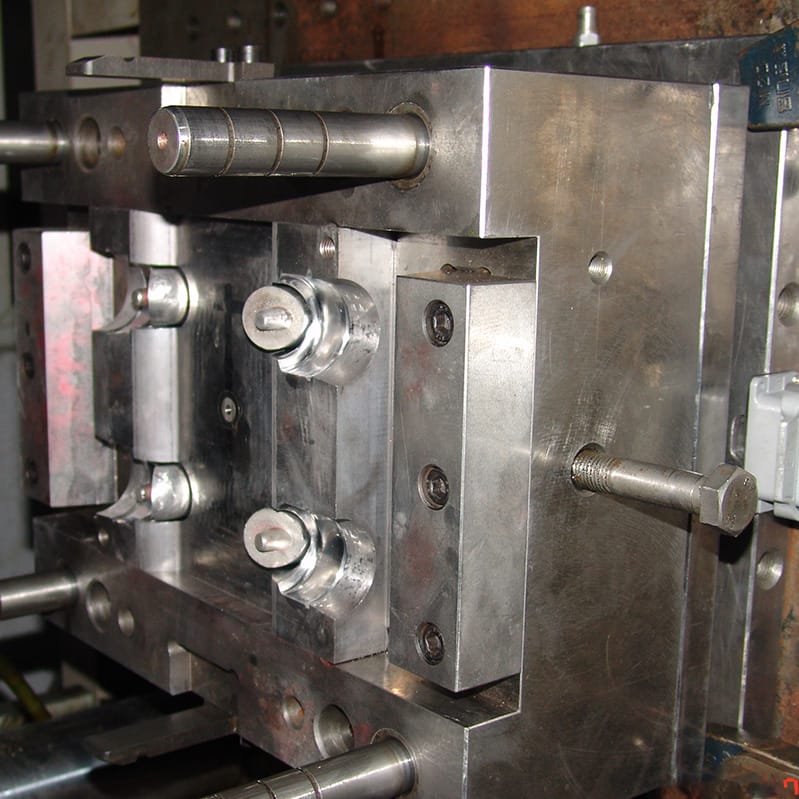
Fitting moulds (or fitting tools or dies) are used during pipe fittings manufacturing to shape and form molten material into desired fitting designs.
Our experienced die and tooling department personnel use their years of combined experience in custom mould design to deliver precise tooling results for plastic injection tooling and prototyping applications. We efficiently meet customer quality demands.
Types of fitting molds:
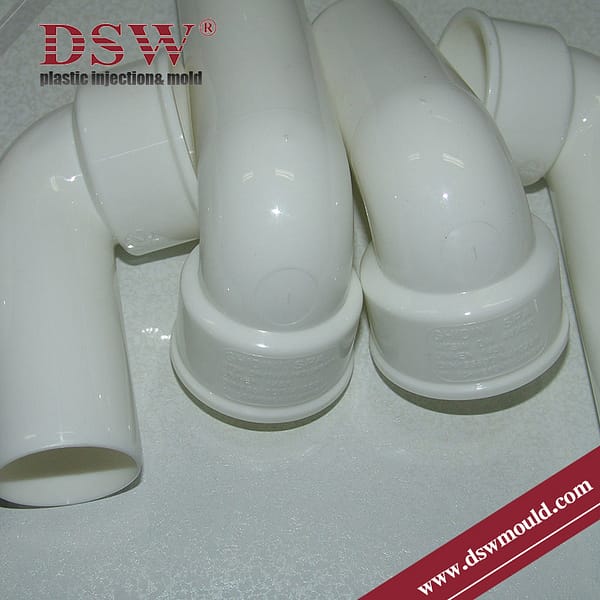
- Elbow Mold: Elbow moulds produce pipe fittings with curved bends at 90 or 45 degrees, typically for 90 and 45-degree angles, respectively. Elbow molds can be designed for various pipe diameters and angles to produce various elbow fittings.
- Tee Mold: Tee molds produce tee-shaped pipe fittings featuring three openings, an inlet, and two outlets arranged in a T shape. Tee moulds can be designed for various pipe diameters and configurations—for instance, an equal or reducing tee fitting would need different measurements than another type.
- Coupling Mold: Coupling molds produce straight pipe fittings that connect two pipes. They typically feature cylindrical or barrel-shaped fittings with female threads for connection or smooth ends that facilitate the connection process.
- Cross Mold: Cross molds are used to produce cross-shaped fittings. Cross fittings feature four openings: an inlet and three outlets arranged crosswise. Cross moulds can be designed for various pipe diameters and configurations.
- Reducer Mold: Reducer molds make pipe fittings that allow size transition between two pipes of different diameters, either gradually or offset. Reducers may have concentric (gradual size transition) or eccentric (offset) transition points and can, therefore, produce various reducer fittings.
- Cap Mold: Cap molds produce end caps or plugs to seal off pipe ends. Flat and dome-shaped fittings may also be used to close off unwanted pipe openings.
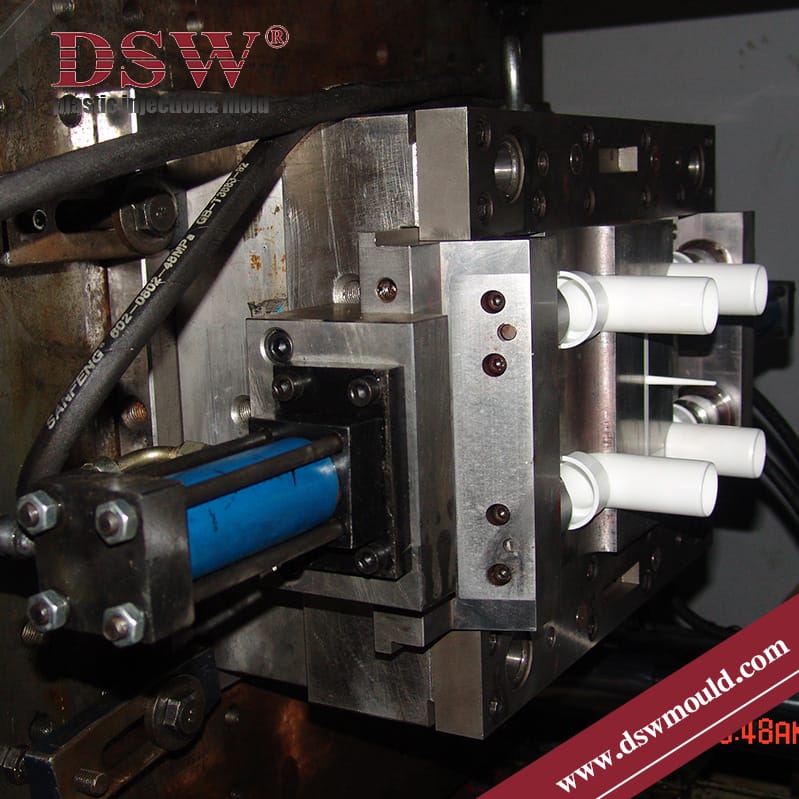
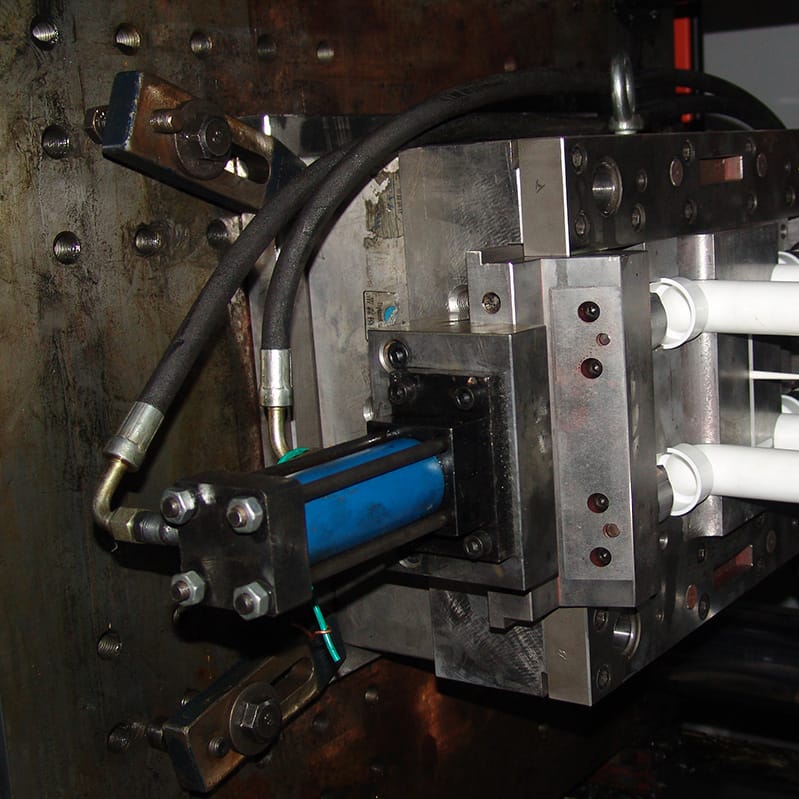
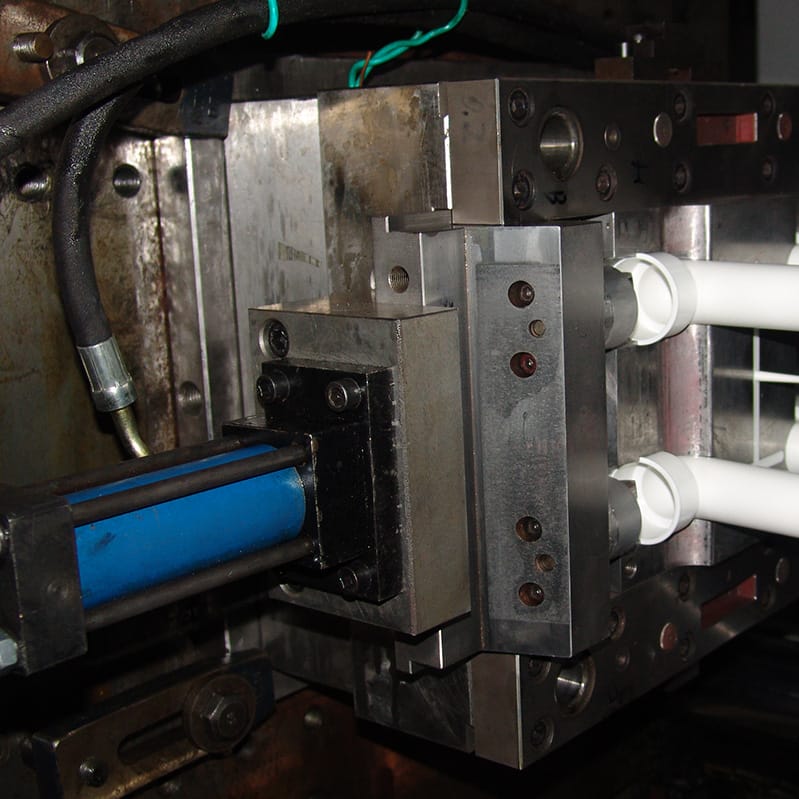
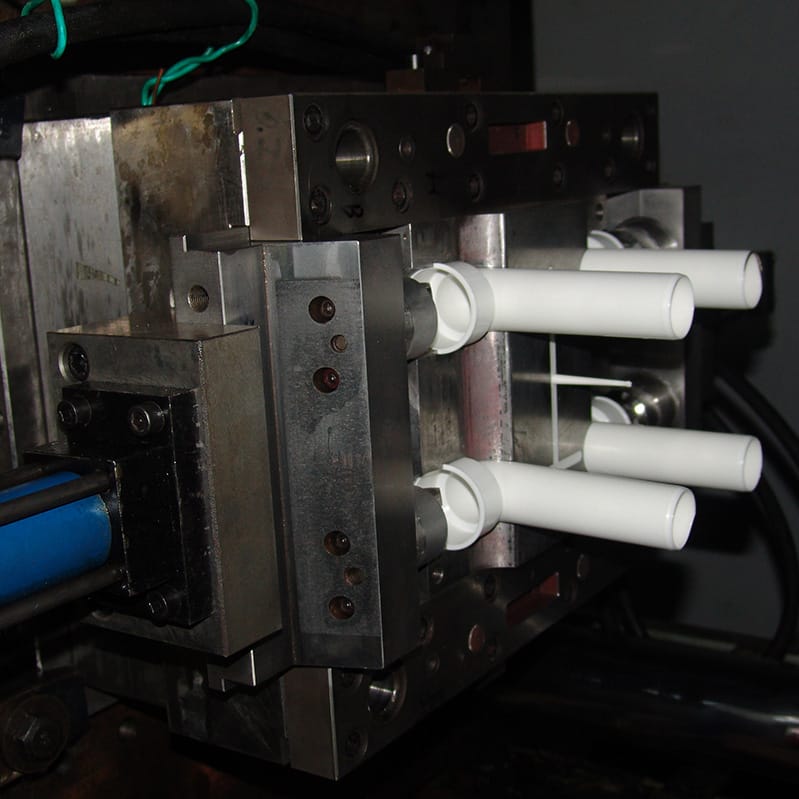
PVC Pipe Fitting mold
| Export to(Country) | USA |
| Tool Description | Injection Mould |
| Material Type | PVC Pipe |
| Cavitation | 4 |
| Weight of Plastic Product | 301g/pcs |
| Mould Design by | DSW |
| Mould Construction | Standard |
| Mould Base | LKM |
| Cav.Material | NAK 80 |
| Core Material | 2738 |
| Side Action | Mechanical Slide |
| Ejection | EJ pins |
| Mould Life | 500,000 |
| Moulded Part Inspection By | DSW |
Injection Molding PVC pipe fittings
Injection moulding PVC pipe fittings offer several advantages, including precise dimensional control, efficient production rates, and the capability of producing complex shapes.
PVC pipe fitting molding process:
PVC pipe fitting moulding is a manufacturing technique that produces polyvinyl chloride (PVC) pipe fittings such as elbows, tees, couplings, and valves. These fittings are essential for plumbing, drainage, irrigation, and other piping systems. The process typically involves injection or compression moulding, where PVC material is shaped into desired pipe fittings under controlled conditions.
PVC compoundRaw PVC resin is usually combined with additives to improve its strength, durability, and processing ease. Common additions include stabilizers, plasticizers, lubricants and pigments.
Melting and Plasticizing:PVC compound is fed into an injection moulding machine’s heated barrel, gradually heating until it becomes dense enough for injection moulds. As it moves through this barrel, its contents become increasingly dense as more heat is applied until finally melting and plasticization occur.
Mould Design: Moulds are pre-designed shapes that determine the final form of pipe fittings. They typically match up with specific pipe fittings needed, such as elbows, tees, or reducers, with precise dimensions to ensure they fit snugly on pipes.
Injection Moulding Process:Filling the Mould: Once PVC has reached a molten state, it is injected under high pressure into a mould cavity using either a ram or screw mechanism and ensures that its entire volume fills the cavity of the mould.
Cooling and Solidifying: After being placed into the mould, PVC material is cooled by passing water or air through it to help harden into shape and harden to its final state.
Ejection: Once the PVC has set completely, the mould opens, and ejector pins or other mechanisms force out the completed fitting from within it.